|

& Links |

|

|

|

|
|
Sample Datasets for Practice |
|
Project Gutenberg
Twitter Posts with #SMU
Congressional Record
Hymnary.org
|
|
Named Entity Recognition (Some places around the world I have visited) contents='' # Load spaCy and displaCy for English content import spacy, en_core_web_sm from spacy import displacy nlp = en_core_web_sm.load() # Render inline from variable contents displacy.render(nlp(contents), jupyter=True, style='ent')Location Frequencies
from collections import Counter
docs = nlp(contents)
# Create list of tuples containing text and entity label
entities = [(X.text, X.label_) for X in docs.ents]
# Store each list of tuples in cumulative list
# full_entities=full_entities+entities
# Create list of labels
labels = [x.label_ for x in docs.ents]
# Store each list of labels in cumulative list
# full_labels=full_labels+labels
print(len(entities), 'entities found')
print(Counter(labels),'\n______\n')
# Frequencies of GPE and LOC Locations Passed to locations_list
print('Frequencies of GPE and LOC Locations')
locations=[]
locations_list=[]
for entity in entities:
if entity[1]=='GPE' or entity[1]=='LOC':
locations.append(entity)
locations_list.append(entity[0])
locations_d=Counter(locations_list)
display(Counter(locations).most_common())
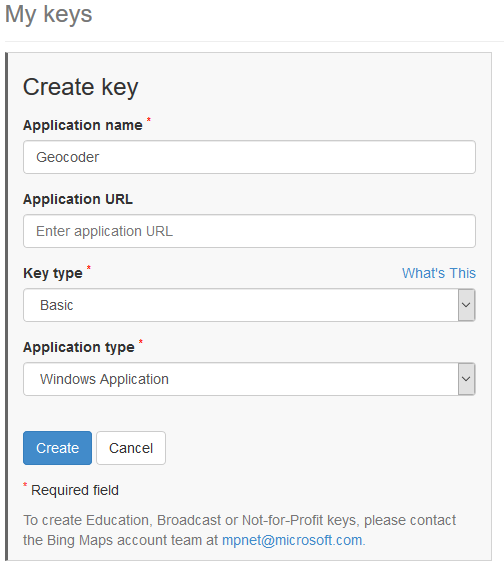
Geocode Addresses Using Bing Maps API
# Enter Bing Maps Key Below
bkey=''
try:
import geocoder
except:
!pip install geocoder
import geocoder
if bkey!='':
for key, value in locations_d.items():
g = geocoder.bing(key, key=bkey)
location=[g.lat, g.lng]
print(key, location)
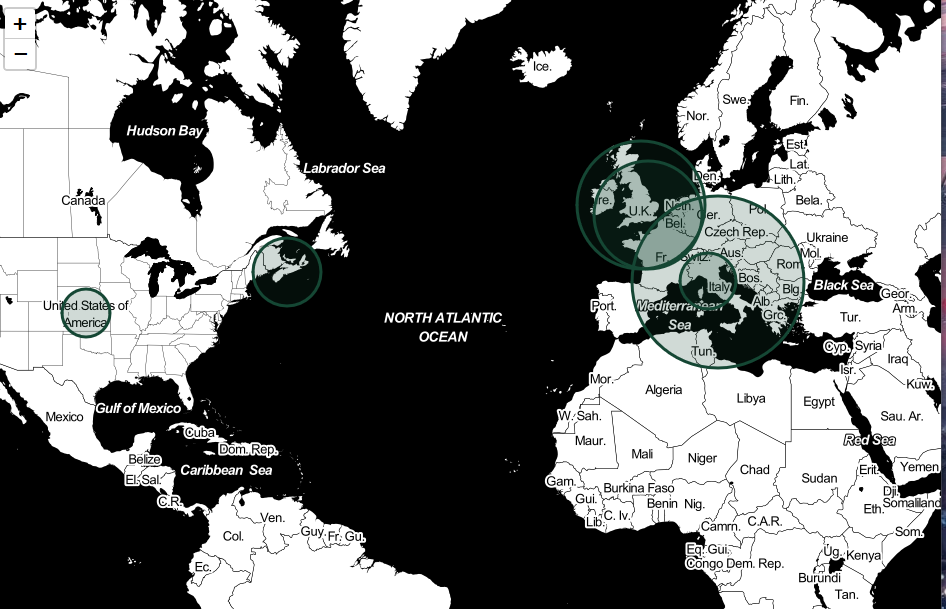
Geocode and Create Interactive Map
# Specify Options Below
#######################
bkey=''
min_location_counts_map = 1 # minimum frequency for mapping
map_base_type = 'Open Street Map' # options: Stamen Toner, Stamen Terrain, Stamen Watercolor, Open Street Map
zoom_default=2
start_location=[31.51073, -96.4247] # U.S. 31.51073, -96.4247, World 0,0, Texas 31.1351682, -99.3350552
geocode_confidence=['High'] # options: High, Medium, Low - Format: ['High','Medium','Low]
radius_multiplier=25
outline_color='#154734'
fill_polygon_color='#154734'
#######################
try:
import geocoder
except:
!pip install geocoder
import geocoder
import folium
if bkey!='':
m = folium.Map(
location=start_location,
zoom_start=zoom_default,
tiles=map_base_type
)
for key, value in locations_d.items():
try:
if value>=min_location_counts_map:
g = geocoder.bing(key, key=bkey)
if g.raw['confidence'] in geocode_confidence:
folium.CircleMarker(
location=[g.lat, g.lng],
radius=value*radius_multiplier,
popup=key+' '+str(value),
tooltip=key+' '+str(value),
color=outline_color,
fill=True,
fill_color=fill_polygon_color
).add_to(m)
except:
pass
display(m)
m.save('index.html')
Upload to Google Colab & Read File(Add to Top) (Use Twitter Sample) from google.colab import files # Browse/Upload File up=files.upload() # File passed to variable doc doc=next(iter(up)) # Read a file using the variable doc f=open(doc, 'r') # Pass into variable named contents contents=f.read() # close connection to file f.close()Specifry URL (Add to Top) (Search for Trump Speech Transcript)
url = ''
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# define header or pages may refuse connection
header = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/39.0.2171.95 Safari/537.36'}
htmlContent = requests.get(url, headers=header)
# remove tags using beautiful soup
contents = BeautifulSoup(htmlContent.text, "lxml").text
# remove line breaks and tab symbols
contents=contents.replace('\n',' ').replace('\r','').replace('\t','')
print('Successfully acquired content from',url)
|
Use Prepared NotebookHandles Larger Files & Zipped Document Collections
|
|
Access via Google Colaboratory (Python environment) View on Github (read only) |
Python Libraries Used
|